Cardiovascular health is a critical aspect of overall well-being, and understanding the differences between atherosclerosis and arteriosclerosis is essential for prevention, diagnosis, and treatment. While these terms are often used interchangeably, they refer to distinct conditions that affect the arteries in different ways. This blog will explore the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for both atherosclerosis and arteriosclerosis.
While also highlighting how cutting-edge AI imaging services, like those offered at Ascend Imaging Center, can play a pivotal role in early detection and management. Lastly, this blog will help you in understanding atherosclerosis vs arteriosclerosis.
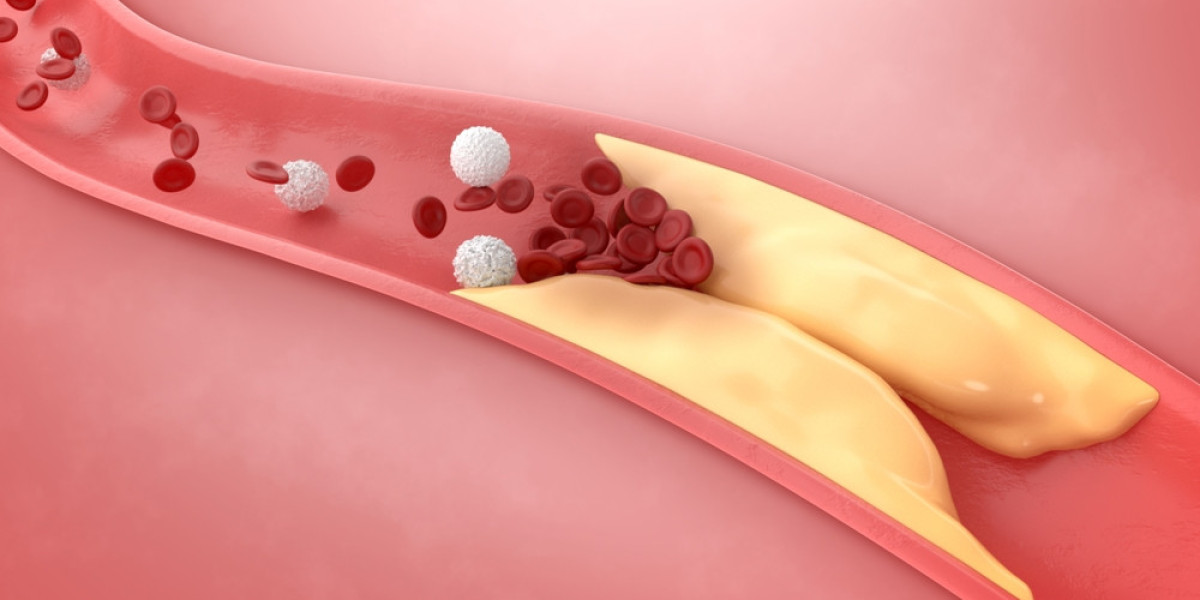
What is Atherosclerosis?
Atherosclerosis is a specific type of arteriosclerosis characterized by the buildup of plaque inside the arterial walls. This plaque is made up of fat, cholesterol, cellular waste, and other substances. Over time, the plaque hardens and narrows the arteries, restricting blood flow to vital organs and tissues. If left untreated, atherosclerosis can lead to serious complications such as heart attack, stroke, or peripheral artery disease.
Causes of Atherosclerosis
- High cholesterol levels (LDL or "bad" cholesterol)
- High blood pressure
- Smoking
- Diabetes
- Obesity
- Sedentary lifestyle
- Genetics and family history
Symptoms of Atherosclerosis
In the early stages, atherosclerosis often presents no symptoms. However, as the condition progresses, symptoms may include:
- Chest pain (angina)
- Shortness of breath
- Fatigue
- Pain or numbness in the limbs
- Erectile dysfunction in men
Treatment of Atherosclerosis
- Lifestyle changes: Adopting a heart-healthy diet, exercising regularly, quitting smoking, and managing stress.
- Medications: Statins to lower cholesterol, blood pressure medications, and antiplatelet drugs to prevent blood clots.
- Surgical procedures: Angioplasty, stenting, or bypass surgery in severe cases.
What is Arteriosclerosis?
Arteriosclerosis is a broader term that refers to the thickening, hardening, and loss of elasticity in the arterial walls. Unlike atherosclerosis, which involves plaque buildup, arteriosclerosis is primarily caused by aging and long-term wear and tear on the arteries. This condition can affect blood flow and increase the risk of cardiovascular events.
Causes of Arteriosclerosis
- Aging
- High blood pressure
- Chronic kidney disease
- Diabetes
- Smoking
- High levels of calcium in the blood
Symptoms of Arteriosclerosis
Similar to atherosclerosis, arteriosclerosis may not show symptoms initially. However, as the arteries become stiffer and narrower, symptoms may include:
- High blood pressure
- Reduced blood flow to organs
- Cold extremities
- Leg pain during physical activity (claudication)
Treatment of Arteriosclerosis
- Lifestyle modifications: Healthy diet, regular exercise, and smoking cessation.
- Medications: Blood pressure-lowering drugs, cholesterol medications, and calcium channel blockers.
- Monitoring: Regular check-ups to assess cardiovascular health.
Key Differences Between Atherosclerosis and Arteriosclerosis
While both conditions affect the arteries, they differ in their underlying mechanisms:
- Atherosclerosis involves plaque buildup and is a specific type of arteriosclerosis.
- Arteriosclerosis is a general term for arterial hardening and can occur without plaque formation.
The Role of Cutting-Edge AI Imaging Services
Early detection and accurate diagnosis are crucial for managing both atherosclerosis and arteriosclerosis. At Ascend Imaging Center, cutting-edge AI imaging services are revolutionizing the way these conditions are diagnosed and monitored. Advanced imaging techniques, such as CT angiography, MRI, and ultrasound, provide detailed visuals of the arteries, allowing healthcare providers to identify plaque buildup, arterial stiffness, and other abnormalities with precision.
AI-powered imaging tools enhance the accuracy of diagnoses by analyzing complex data and detecting subtle changes that may be missed by traditional methods. This technology enables personalized treatment plans and improves patient outcomes by catching cardiovascular issues at their earliest stages.
Prevention Tips for Atherosclerosis and Arteriosclerosis
Focus on a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins to support heart health. Incorporate foods high in omega-3 fatty acids, such as salmon and walnuts, to reduce inflammation. Limit intake of saturated fats, trans fats, and processed foods, which can contribute to plaque buildup. Opt for low-sodium options to manage blood pressure and reduce strain on the arteries. Other than that, one should:
1. Maintain a Healthy Diet
2. Exercise Regularly
3. Avoid Smoking and Limit Alcohol Consumption
4. Manage Chronic Conditions
5. Schedule Regular Check-Ups and Screenings
6. Maintain a Healthy Weight
7. Reduce Stress Levels
8. Stay Hydrated and Limit Caffeine
9. Educate Yourself and Stay Informed
10. Get Adequate Sleep
By incorporating these prevention tips into your daily routine, you can significantly reduce your risk of developing atherosclerosis and arteriosclerosis. Prioritizing heart health through proactive measures and regular monitoring is the key to maintaining a healthy cardiovascular system for years to come.
Wrapping It Up
Understanding the differences between atherosclerosis and arteriosclerosis is vital for protecting your cardiovascular health. While both conditions can lead to serious complications, early detection, and proactive management can significantly reduce risks. By leveraging cutting-edge AI imaging services, such as those offered at Ascend Imaging Center, patients can benefit from accurate diagnoses and tailored treatment plans. Prioritizing heart health through lifestyle changes and regular monitoring is the key to preventing and managing these conditions effectively.
Whether you're at risk for atherosclerosis or arteriosclerosis, staying informed and taking proactive steps can make all the difference. Explore the advanced imaging services available at Ascend Imaging Center to take control of your cardiovascular health today. We offer cutting-edge AI imaging services at our imaging center. Visit at the earliest to make it easier on yourself through and through.
FAQs
What is the difference between atherosclerosis and arteriosclerosis?
Atherosclerosis is a specific type of arteriosclerosis involving plaque buildup in the arteries, composed of fat, cholesterol, and other substances. Arteriosclerosis is a broader term referring to the thickening and hardening of arterial walls, often due to aging or high blood pressure. While atherosclerosis narrows arteries due to plaque, arteriosclerosis causes stiffness and loss of elasticity. Atherosclerosis is a subset of arteriosclerosis, but not all arteriosclerosis involves plaque. Both conditions restrict blood flow but have different underlying causes and mechanisms.
What is the treatment of arteriosclerosis?
Treatment for arteriosclerosis focuses on managing symptoms and preventing progression. Lifestyle changes like a heart-healthy diet, regular exercise, and quitting smoking are essential. Medications such as blood pressure-lowering drugs, cholesterol medications, and calcium channel blockers may be prescribed. Managing underlying conditions like diabetes or high blood pressure is crucial. In severe cases, surgical interventions like angioplasty may be needed. Regular monitoring and check-ups help track the condition and adjust treatment plans as necessary.
What are the main symptoms of atherosclerosis?
There are various symptoms of atherosclerosis, these include but are not limited to the below listed few:
1. Chest pain (angina) due to reduced blood flow to the heart.
2. Shortness of breath, especially during physical activity.
3. Fatigue caused by inadequate oxygen supply to tissues.
4. Pain or numbness in limbs, indicating peripheral artery involvement.
What is the difference between atherosclerosis and sclerosis?
Atherosclerosis specifically refers to plaque buildup in the arteries, leading to narrowing and reduced blood flow. Sclerosis is a general term meaning the hardening or thickening of tissue, which can occur in various parts of the body, not just arteries. Atherosclerosis is a type of sclerosis affecting the arterial walls, while sclerosis can refer to conditions like multiple sclerosis (affecting nerves) or bone sclerosis. The key difference is the location and specific cause of the hardening or thickening.